CBD, Health and Wellness
What Is CBD?
In this article, you’ll learn and discover what is CBD.
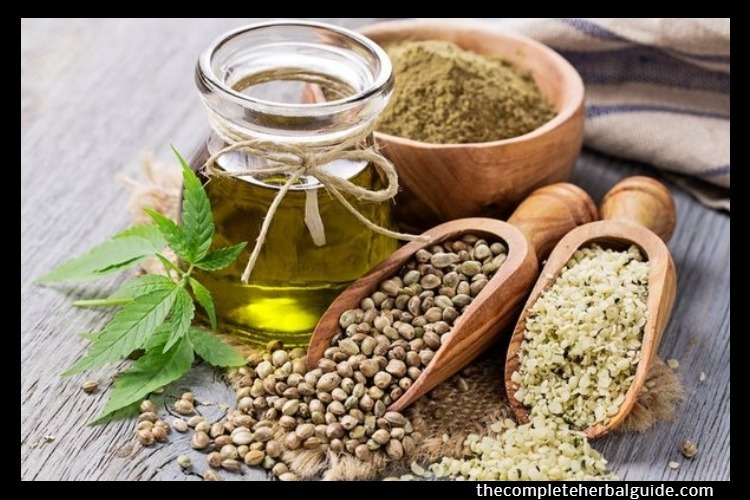
CBD is one of over 60 compounds found in cannabis that belong to a class of ingredients called cannabinoids. Until recently, THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) was getting most of the attention because it’s the ingredient in cannabis that produces mind-altering effects in users, but CBD is also present in high concentrations — and the medical world is realizing that its list of medical benefits continues to grow.
CBD is the major nonpsychoactive component of Cannabis sativa. According to a 2013 study published in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, CBD benefits including acting in some experimental models as an anti-inflammatory, anticonvulsant, antioxidant, antiemetic, anxiolytic, and antipsychotic agent, and is, therefore, a potential medicine for the treatment of…
- neuroinflammation
- epilepsy
- oxidative injury
- vomiting
- nausea
- anxiety
- schizophrenia
Research
Studies are beginning to show that CBD is different than other well-studied cannabinoids. All cannabinoids act as ligands, meaning they dock onto the binding site of a protein and have the ability to modulate a receptor’s behavior. CB1 receptors are widely distributed but are particularly abundant in areas of the brain, including those concerned with movement, coordination, pain and sensory perception, emotion, memory, cognition, autonomic and endocrine functions.
CB2 receptors are found mostly in the immune system, and they seem to reduce inflammation and certain kinds of pain. Although cannabinoids all have similar structures, they display a wide array of actions at each of the different receptors.
What Scientists Say
However, scientists are finding out that CBD has a very little effect on CB1 and CB2 receptors, which probably explains why it doesn’t have mind-altering effects, unlike THC, which positively regulates the CB1 receptor. That’s why most marijuana grown for recreational purposes are typically very low in CBD and high in THC.
Check our bestsellers!
WHAT’S YOUR #1 HEALTH GOAL?
When you sign up for our email list today, you also get 3 eBooks free: